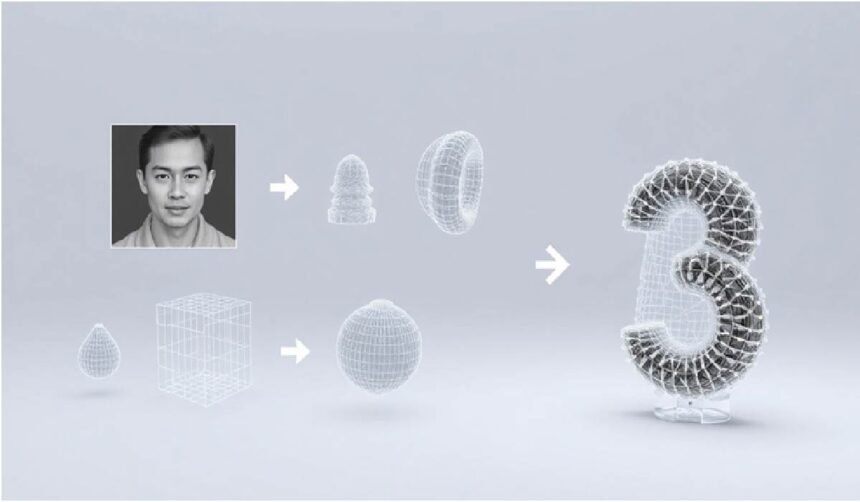
The Evolution of 2D To 3D Conversion
Turning a flat picture into a fully-fledged 3D asset used to be a big deal. It was a complex process, mostly for specialists. Now, AI is changing all that. This technology takes a simple photograph and lets an algorithm figure out its depth, texture, and shape to build a digital model. This ability to convert picture to 3D is making things much faster for everyone.
This process, once only for technical artists, is now available to more people. It’s a practical reality now. Modern AI tools have made this a real option, turning a task that took ages into a quick step in the creative process. The tools highlighted in 3DAIStudio’s guide show how creators can now How to turn photos into 3D models using streamlined AI workflows that make detailed 3D output achievable in minutes. For digital artists, game developers, and e-commerce brands, this means a big jump in efficiency.
AI’s Role in Streamlining 3D Asset Creation
AI is really shaking things up in how we make 3D stuff. It automates the tricky parts of modeling. This means teams can get from idea to finished product much quicker. It removes technical hurdles, letting people try out more ideas without needing expert modeling skills. This new ease means teams can add 3D content to their projects without causing big delays.
AI acts as the bridge between a simple 2D picture and a complex 3D model. It handles the hard technical work. This lets your team focus on the creative side. The goal is to show that making good 3D models from existing images isn’t just possible—it’s a real advantage for how businesses operate.
Bridging The Gap Between Images And Models
AI is really good at interpreting what it sees in a photo. It looks at light, shadow, and color to build a 3D form. If a photo has dark shadows or blurry details, the AI gets confused. This can lead to wrong results. Providing clear, unambiguous information about the object’s shape is key.
Soft, even lighting is best. It lights up the subject without creating deep shadows. These shadows can trick the AI into thinking there are holes or weird shapes. A product photo taken in a lightbox, for example, will almost always work better than one taken in bright sunlight. Hard shadows can make the AI create dents or warp the model’s surface.
The quality of the final 3D model often depends more on the input image than the AI itself. Some simple preparation can make a big difference in the outcome.
Preparing Your Images For Optimal AI Conversion
The Impact Of Lighting And Shadows
Getting the lighting right is a big deal when you want to convert picture to 3D. The AI looks at light and dark areas to figure out shapes. If you have really harsh shadows, the AI might think those shadows are actually part of the object. This can make the 3D model look weird, like it has dents or bumps where there shouldn’t be any. Soft, even light is the best way to go. Think about using a lightbox or shooting on a cloudy day. This makes sure the object is lit up nicely without confusing shadows.
Good lighting helps the AI see the object’s true form. It’s not about making the photo look pretty; it’s about giving the AI clear information. If you use a photo taken in bright, direct sun, you’re probably going to get a 3D model that looks a bit messed up. The AI can’t guess what’s under a deep shadow, so it just makes something up, and usually, it’s not what you want. So, pay attention to how light hits your subject.
This is why product photos taken in controlled lighting conditions often convert so well. They’re designed to show the product clearly. When you prepare your images, aim for that same clarity. Avoid strong contrasts that could trick the AI into creating unwanted geometry. The goal is to present the object’s shape as plainly as possible.
Achieving High-Resolution Image Specifications
When you convert picture to 3D, more pixels mean more detail for the AI to work with. It’s like giving the AI a sharper picture to look at. If you use a low-resolution image, the AI won’t have enough information to create a detailed 3D model. You’ll end up with something that looks blocky or lacks fine features. Aim for images that are at least 1024×1024 pixels, but bigger is usually better. This gives the AI a much better chance to capture the nuances of the object.
Think of it this way: the AI is trying to build a 3D object based on a 2D image. If the image is blurry or lacks detail, the AI has to fill in a lot of blanks. This often leads to a less accurate final model. High-resolution images provide the necessary data for the AI to construct a more faithful representation of the object. It’s a simple principle: better input leads to better output.
So, before you start the conversion process, check your image resolution. Make sure it meets the recommended specifications for the AI tool you’re using. A few extra minutes spent ensuring your images are high-resolution can save you a lot of time and frustration later on when you’re trying to fix a low-detail 3D model.
Choosing The Right File Format For Conversion
When you’re getting ready to convert picture to 3D, the file format matters. Some formats are better than others because they don’t lose any image quality. PNG is a good choice because it’s a lossless format. This means it keeps all the original detail from your photo, which is exactly what the AI needs. JPEGs can work, but only if they’re high quality. If a JPEG has been compressed too much, it can create weird blocky patterns, and the AI will pick those up, leading to problems in the 3D model.
It’s like trying to build something with slightly damaged building blocks. The AI will try its best, but those imperfections in the image file will show up in the final 3D model. You want to give the AI the cleanest possible data. Using a lossless format like PNG helps avoid introducing unnecessary noise or artifacts into the conversion process. This is a key step in getting a clean conversion.
So, always try to save your images in a format that preserves quality. PNG is generally the safest bet for most AI 3D conversion tools. Avoid heavily compressed formats if you can. This simple choice can make a significant difference in the quality of the 3D model you get back from the AI.
Understanding AI Capabilities And Limitations
Setting Realistic Expectations For Detail
AI is a powerful tool for converting 2D images into 3D models, but it’s not magic. The AI analyzes the visual information present in your photos to infer depth and form. It cannot invent details that aren’t suggested by the source material. If an object has very fine, intricate patterns or subtle textures, the AI might simplify them or miss them entirely. Think of it like trying to draw a detailed portrait from a blurry photograph – you can get the likeness, but the tiny nuances might be lost. This means that for highly complex or delicate designs, you might still need some manual touch-ups.
The Collaborative Process Between AI And Artist
Modern AI 3D conversion works best as a partnership. The AI can rapidly generate a base model, saving artists significant time on repetitive tasks. However, the artist’s eye is still needed for refinement. This collaboration allows for faster iteration and a higher quality final product. The AI handles the heavy lifting of geometry creation, while the artist focuses on adding the finer details, correcting any inaccuracies, and ensuring the model fits the intended use case. This synergy is key to achieving professional results.
Identifying Ideal Objects For AI Conversion
Some objects lend themselves better to AI conversion than others. Objects with clear, defined shapes and good lighting in the source images tend to produce the best results. Think of everyday items like furniture, simple geometric shapes, or even well-photographed consumer products. Items with highly reflective surfaces, transparent materials, or extremely complex, organic forms can present more challenges for current AI systems. Understanding these preferences helps you choose subjects that will yield the most successful 3D models with minimal post-processing.
The quality of the AI’s output is directly tied to the quality and clarity of the input images. Garbage in, garbage out, as they say. Providing well-lit, high-resolution photos from multiple angles will always yield better results than a single, poorly lit snapshot.
Here’s a quick look at what works well:
- Solid, Opaque Objects: Things like statues, mugs, or books.
- Objects with Clear Silhouettes: Easily distinguishable shapes.
- Well-Lit Subjects: Even lighting without harsh shadows.
And here are some areas where AI might struggle:
- Highly Reflective Surfaces: Like mirrors or polished chrome.
- Transparent Materials: Glass or clear plastics.
- Extremely Fine Details: Lace, intricate filigree, or very thin wires.
Troubleshooting Common Conversion Errors
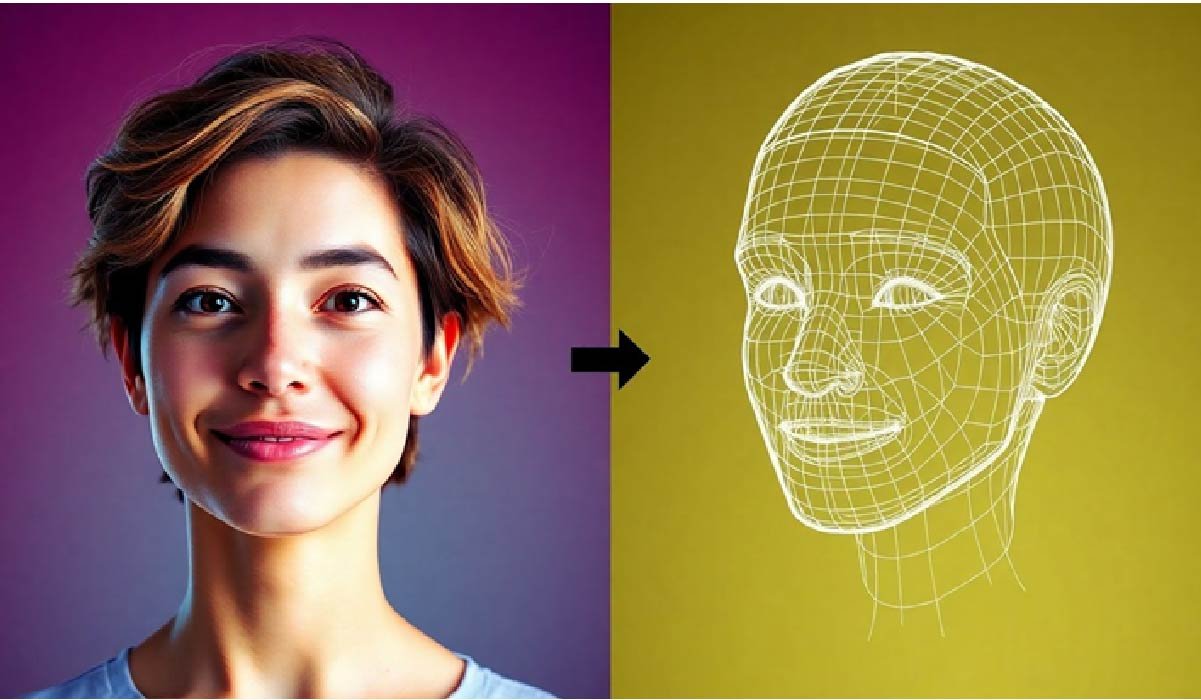

Even with the best preparation, sometimes the AI conversion doesn’t quite hit the mark. Don’t worry, this is normal. Most issues stem from the source image or the AI’s interpretation of it. Understanding these common problems helps you fix them faster.
Addressing Warped Or Melted Geometry
Warped or “melted” geometry is a frequent headache. This often happens when the AI misinterprets harsh shadows or highlights as part of the object’s actual shape. Think of a shiny object under direct sunlight; the bright spots and deep shadows can confuse the AI, leading it to create bumps or indentations where there should be a smooth surface. The key is to provide clear, even lighting in your source image. Soft, diffused light, like that from a lightbox or an overcast day, prevents these misinterpretations. If you see this issue, review your original photo’s lighting. Was it too harsh? Were there strong, dark shadows? Adjusting the lighting in your source image and re-running the conversion is usually the first step to fixing warped geometry.
Identifying Issues With Source Image Quality
Poor source image quality is the root of many conversion problems. If your image is low-resolution, blurry, or has a busy background, the AI struggles to get a clear picture of the object. It’s like trying to describe something you can barely see – the description will be vague and inaccurate. For instance, a fuzzy image of a chair might result in a 3D model with indistinct legs or a poorly defined seat. The AI can’t invent details that aren’t there. Therefore, always aim for high-resolution images with sharp focus and a clean, uncluttered background. A simple, solid-colored background helps the AI isolate the subject, leading to a much cleaner conversion. Remember, the quality of your input directly impacts the quality of your output when you convert picture to 3D.
Strategies For Corrective Workflows
When a conversion isn’t perfect, a systematic approach to correction is needed. First, analyze the output model. Rotate it, inspect it from all angles, and compare it against your source image. Look for specific problems: Is the overall shape correct? Are there any strange artifacts or holes? Did the AI capture the important details? Based on your findings, you might need to adjust settings like mesh density or detail level in your AI tool. Sometimes, a simple re-generation with a slightly tweaked source image is all it takes. For more complex issues, manual cleanup in 3D modeling software might be necessary. This iterative process of generating, assessing, and refining is how you achieve a polished final model. It’s a collaboration between the AI’s power and your artistic judgment.
Leveraging AI For Enhanced Creative Workflows
Accelerating Game Development Pipelines
Modern AI tools are changing how game developers build worlds. The ability to convert a 2D image to 3D asset means concept art can become game-ready models much faster. This speeds up the entire production cycle, letting teams focus more on gameplay and less on the technical side of asset creation. This new workflow makes creating detailed 3D models from existing images a real advantage.
Revolutionizing E-commerce Product Visualization
For online stores, showing products in 3D is a game-changer. AI makes it simple to turn standard product photos into interactive 3D viewers. Customers can then examine items from every angle, leading to better understanding and fewer returns. This AI-powered approach helps brands present their products in a more engaging and informative way.
Adding Depth To Digital Art Projects
Digital artists can now introduce a new level of realism and depth to their work. By using AI to generate 3D elements from 2D images, artists can create more complex scenes and characters. This technology opens up new creative possibilities, allowing for richer visual storytelling and more immersive digital experiences. The speed at which these 3D models can be generated is truly remarkable.
Exploring Advanced AI 3D Generation Techniques
Utilizing Multiview Capabilities For Accuracy
Modern AI 3D generation tools are getting smarter. While a single image can give you a decent model, using multiple views really ups the ante. Think of it like showing a sculptor a picture from the front, side, and back – they get a much clearer idea of the whole object. This approach helps the AI understand depth and form much better, reducing guesswork.
The more angles you provide, the more accurate and complete your 3D model will be. This is especially true for complex shapes or objects with intricate details that might be hidden from a single viewpoint. It’s a simple step that makes a big difference in the final output.
Integrating AI Generation Into Existing Pipelines
Getting AI-generated 3D models into your current workflow is becoming easier. Many platforms now offer APIs, which are like bridges that let your existing software talk to the AI. This means you don’t have to manually move files back and forth all the time.
This integration speeds things up considerably. Instead of spending hours exporting and importing, you can generate assets directly within your 3D software or game engine. It makes the whole process feel more natural and less like a separate step.
The Speed Revolution In 3D Asset Creation
We’re seeing a massive shift in how fast 3D assets can be made. What used to take days or weeks can now happen in minutes, thanks to AI. This speed isn’t just about saving time; it changes how creative projects are approached.
Imagine generating dozens of variations for a game character or product visualization in the time it used to take to make one. This rapid iteration allows for more experimentation and refinement, leading to better final results. The speed of AI 3D generation is truly a game-changer for creators.
The Future is 3D, and AI is Leading the Way
So, turning a flat picture into a 3D model used to be a big deal, something only pros could really do. But now? AI has changed all that. It’s like magic, taking a simple photo and figuring out its shape and texture to build a digital object. This means artists, game makers, and online shops can create 3D stuff way faster and easier than before. You don’t need to be a 3D wizard anymore. Just get your image ready – good lighting and clear focus are key – and let the AI do the heavy lifting. It’s not just about making things look cool; it’s about making the whole creative process quicker and opening up new possibilities for everyone.