Stainless Steel Machining
Stainless steel machining is used in many industries, such as cars, airplanes, and medical tools. It aids in creating good-quality and durable components. It involves cutting, bending, and shaping stainless steel to produce long-lasting and precision-working parts.
In the guide, you will be informed about the principal techniques such as CNC machining, milling, and laser cutting. We are also going to discuss the issues, advantages, and optimal methods of achieving good outcomes.
What Is Stainless Steel Machining
Stainless steel machining refers to cutting and shaping stainless steel into parts. It involves turning, drilling, milling, and laser cutting.
Stainless steel is hard and resistant to rust, thus more difficult to slice as compared to ordinary steel or aluminum. Therefore, it requires the appropriate tools, cooling, and speed to prevent tool damage and overheating. When finished well, it offers good finishes and correct shapes that are applied in most industries.
Machinable Stainless Steel Grades
Not all stainless steels machine easily. The two types respond differently in terms of heat and cutting tools. The simplest of them to machine is of a good combination of hardness and corrosion resistance.
Here are the main types:
Austenitic: Nickel and chromium are abundant in austenitic (300 series). It is not very easy to cut, and it does not rust. Grades 303 and 304 are common.
Martensitic (400 series) contains a higher content of carbon and can be heat-treated. Austenitic is harder to machine than it is.
Ferritic is more machineable and it has medium resistance against corrosion. Grade 430 is applied to automobile and domestic components.
Precipitation-Hardened (PH grades) are highly resistant to rust and very strong. Planes and instruments are used in it.
CNC Machining Stainless Steel

CNC machining involves the use of computers to cut and shape stainless steel using computer-controlled machines. The computer provides instructions as to the movement and cutting of the tools.
Benefits of CNC Machining Stainless Steel
CNC machining has numerous advantages. It produces components of superior quality consistently and manages complicated shapes easily. It reduces human error as well as may operate on hard and thick metals without losing precision.
Challenges
There are challenges associated with it, too. Stainless steel may cause rapid wear of the tools since it contains heat. In order to resolve this, machine operators apply the following: coolants, special carbide cutters, and the correct cutter speed to prevent tool wear.
Speeds and Feeds for Milling Stainless Steel
Milling Stainless steel speed and feeds require balance along with temperature control. Excessive speed causes the tools to wear out. In case it is too slow, the surface will be rough. Maintenance of appropriate temperature prevents hardening and spoiling of the tools.
Stainless Steel Laser Cutting
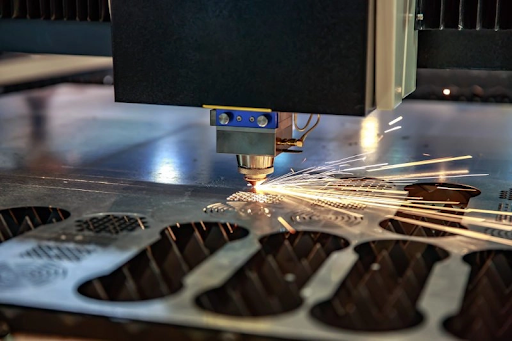
The stainless steel laser cutting involves cutting the metal with a beam of light. The laser burns or evaporation the metal into vapor, creating clean and smooth edges.
The current machine has either CO2, fiber, or Nd: YAG lasers to achieve accurate results. Laser cutting applies to all major stainless steel types.
How It Works
The laser concentrates the energy on a small area, heating or melting the metal. Gases such as nitrogen or oxygen eliminate the melted metal and prevent rusting. The process is controlled by a computer in order to produce correct shapes, holes, or patterns.
Benefits of Stainless Steel Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is precise, repeatable, and provides smooth and burr free edges. It requires minimal finishing and can be used on thin and thick sheets. It also stops work hardening, which occurs in mechanical cutting. This renders laser cutting ideal for the parts that require tight fits and clean and smooth surfaces.
Common Issues and Fixes
Dripping edges occur due to an excessive amount of heat. This can be fixed by changing the focus point or accelerating the speed of the feed. The presence of brown marks is due to oxygen; hence, clean nitrogen gas would help. When there is splashing of the edges, one can decrease air pressure or reduce cutting speed.
CNC vs Laser Machining

CNC machining involves the removal of metal using tools, and laser cutting involves the use of a beam of light. CNC is preferable with dense materials and 3D objects. Laser cutting is more efficient with finer designs and fine sheets.
Laser cutting is more rapid and cleaner, whereas CNC machining can cut deeper and more intricately. The most suitable is based on the type of part required.
Cost and Efficiency
The cost of machining stainless steel is higher than that of mild steel due to a higher rate of wear of the tools and slow machining. However, the contemporary CNC and laser machines are used to save time and boost production.
When compared to the CO2 lasers, fiber lasers are 4-6 times faster in cutting. CNC machines save man-hours and minimize wastage. Coolants and coated tools can also be used to ensure that the tools outlive their usefulness.
A laser cutting machine is more expensive to purchase, yet it produces accurate output and reduces maintenance expenses in the long term.
Conclusion
Stainless steel machining is a set of CNC milling, turning, and laser cutting to produce a high-quality, durable part. Knowledge of material grades, machining parameters, and equipment types is a guarantee of efficient operations and prolonged tool life.
In particular, laser cutting provides outstanding accuracy and clean edges for industrial and commercial purposes. With a proper combination of machine setup and proper machining speeds and feeds, it is possible to obtain the high-quality results of machine work in all machining.







